Indications and Usage
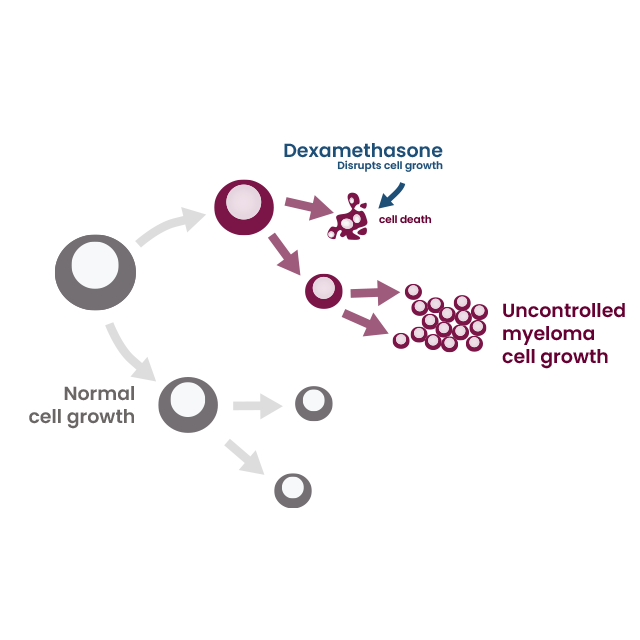
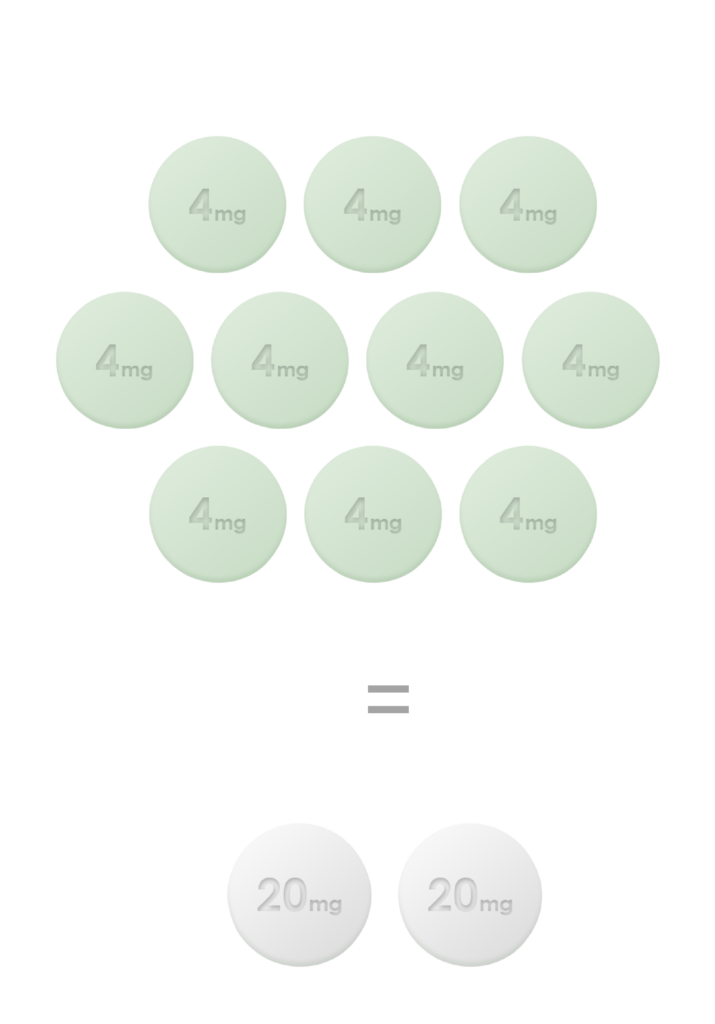
Hemady® (dexamethasone) tablets, 20 mg, is a corticosteroid indicated in combination with other anti-myeloma products for the treatment of adults with multiple myeloma.
Select Important Safety Information for Healthcare Providers
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity: Hemady® is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to dexamethasone, or to any components of this product. Rare instances of anaphylactic reactions have been reported.
Fungal Infections: Hemady® is contraindicated in patients with systemic fungal infections. Corticosteroids may exacerbate systemic fungal infections.
Warnings and Precautions
Alterations in Endocrine Function: Hemady® can cause serious and life-threatening alterations in endocrine function, especially with chronic use. Monitor patients for Cushing’s syndrome and hyperglycemia while receiving corticosteroids and adrenal insufficiency and steroid “withdrawal syndrome” after corticosteroid withdrawal.
Increased Risk of Infection: Corticosteroids, including Hemady®, suppress the immune system and increase the risk of infection with any pathogen, including viral, bacterial, fungal, protozoan, or helminthic pathogens. Corticosteroids can (i) reduce resistance to new infections, (ii) exacerbate existing infections, (iii) increase the risk of disseminated infections, (iv) increase the risk of reactivation or exacerbation of latent infections, (v) mask some signs of infection. Corticosteroid-associated infections can be mild but can be severe and at times fatal. The rate of infectious complications increases with increasing corticosteroid dosages.
Alterations in Cardiovascular/Renal Function: Alterations in cardiovascular and renal function can occur. Monitor for elevated blood pressure and sodium, and decreased potassium levels. Use with caution in patients with congestive heart failure and recent myocardial infarction.
Venous and Arterial Thromboembolism: Thromboembolism is a known adverse reaction of dexamethasone, including Hemady®. When administered with anti-myeloma products (e.g., thalidomide, lenalidomide, pomalidomide, and carfilzomib) the risk for venous and arterial thromboembolism increases significantly. Refer to the prescribing information of these anti-myeloma products. Consider using anticoagulant prophylaxis and monitor for evidence of thromboembolism.
Vaccination: Avoid administration of live or live attenuated vaccines in patients receiving immunosuppressive doses of corticosteroids.
Ophthalmic Effects: Use of corticosteroids including Hemady® may produce posterior subcapsular cataracts, glaucoma with possible damage to the optic nerves, and may enhance the establishment of secondary ocular infections. If steroid therapy is continued for more than 6 weeks, intraocular pressure should be monitored.
Gastrointestinal Perforation: There is an increased risk of gastrointestinal perforation during corticosteroid use in patients with certain gastrointestinal disorders. Avoid corticosteroids such as Hemady® if there is a possibility of impending perforation, abscess, or other pyrogenic infections; diverticulitis; fresh intestinal anastomoses; or active or latent peptic ulcer.
Osteoporosis: Corticosteroids decrease bone formation and increase bone resorption. Special consideration should be given to patients at increased risk of osteoporosis (e.g., postmenopausal women) before initiating Hemady®therapy.
Myopathy: An acute myopathy has been observed with the use of high doses of corticosteroids.
Behavioral and Mood Disturbances: Potentially severe psychiatric adverse reactions may occur with systemic corticosteroids, including Hemady®. Inform patients and caregivers of the potential for behavioral and mood changes and encourage them to seek medical attention if symptoms develop.
Kaposi’s Sarcoma: Kaposi’s sarcoma has been reported to occur in patients receiving corticosteroid therapy, most often for chronic conditions. Discontinuation of corticosteroids may result in clinical improvement of Kaposi’s sarcoma.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Hemady® can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for one month after treatment with Hemady®. Refer to the prescribing information of the combination anti-myeloma product for additional Contraindications, Warnings and Precautions.
Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions are cardiovascular, dermatologic, endocrine, fluid and electrolyte disturbances, gastrointestinal, metabolic, musculoskeletal, neurological/psychiatric, ophthalmic, abnormal fat deposits, decreased resistance to infection, hiccups, increased or decreased motility and number of spermatozoa, malaise, moon face, and weight gain.
Please see Full Prescribing Information for Hemady®.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088 (1-800-332-1088). You also may contact Edenbridge Pharmaceuticals, LLC at 1-877-381-3336.
Hemady® [Prescribing Information]. Edenbridge Pharmaceuticals, LLC. June 2024.
References
- Hemady® [Prescribing Information]. Edenbridge Pharmaceuticals, LLC. June 2024.
- Bashir Q, et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020;20:768-7735.
- Rosenberg AS. Leuk Lymphoma. 2023;64(2):283-291.
- FDA. Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Hemady® New Drug Application. 2019.
- Sharma S, et al. Blood. 2008;112:1338-1345.
- Greenstein S, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:1681-1694.
- Gupta M, et al. Int J Basic Clin Pharmacol. 2013;2:103-121.



 The information on this site is intended for healthcare professionals in the United States, its territories, and Puerto Rico and is not intended for the general public.
The information on this site is intended for healthcare professionals in the United States, its territories, and Puerto Rico and is not intended for the general public.